Breastfeeding is a crucial aspect of newborn care that offers a myriad of benefits for both the baby and the mother. The incredible impact of breastfeeding on newborn development cannot be understated, as it provides essential nutrients and antibodies that contribute to the overall health and well-being of the baby. Let's delve into the significant ways in which breastfeeding influences newborn development:
Nutrient-Rich Milk
Breast milk is a powerhouse of essential nutrients such as proteins, fats, vitamins, and carbohydrates that are crucial for the baby's growth and development. It contains the perfect balance of nutrients that are easily digestible and tailored to meet the baby's evolving needs. Fact: Breast milk also adapts its composition to provide additional antibodies when the mother or baby is sick.
Enhanced Brain Development
Breastfeeding has been linked to enhanced brain development in newborns due to the presence of essential fatty acids like DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). These fatty acids play a vital role in the development of the baby's nervous system and cognitive function, helping to support optimal brain growth. Fact: Studies have shown that breastfed babies have higher IQ scores later in life compared to formula-fed babies.
Boosted Immunity
One of the most significant benefits of breastfeeding is its ability to boost the baby's immune system. Breast milk is rich in antibodies and immune-boosting factors that help protect the baby against infections, allergies, and illnesses. It provides passive immunity that strengthens the baby's immune response and reduces the risk of developing respiratory infections, ear infections, and gastrointestinal issues. Fact: Breastfed babies have a lower risk of developing chronic conditions such as asthma and eczema.
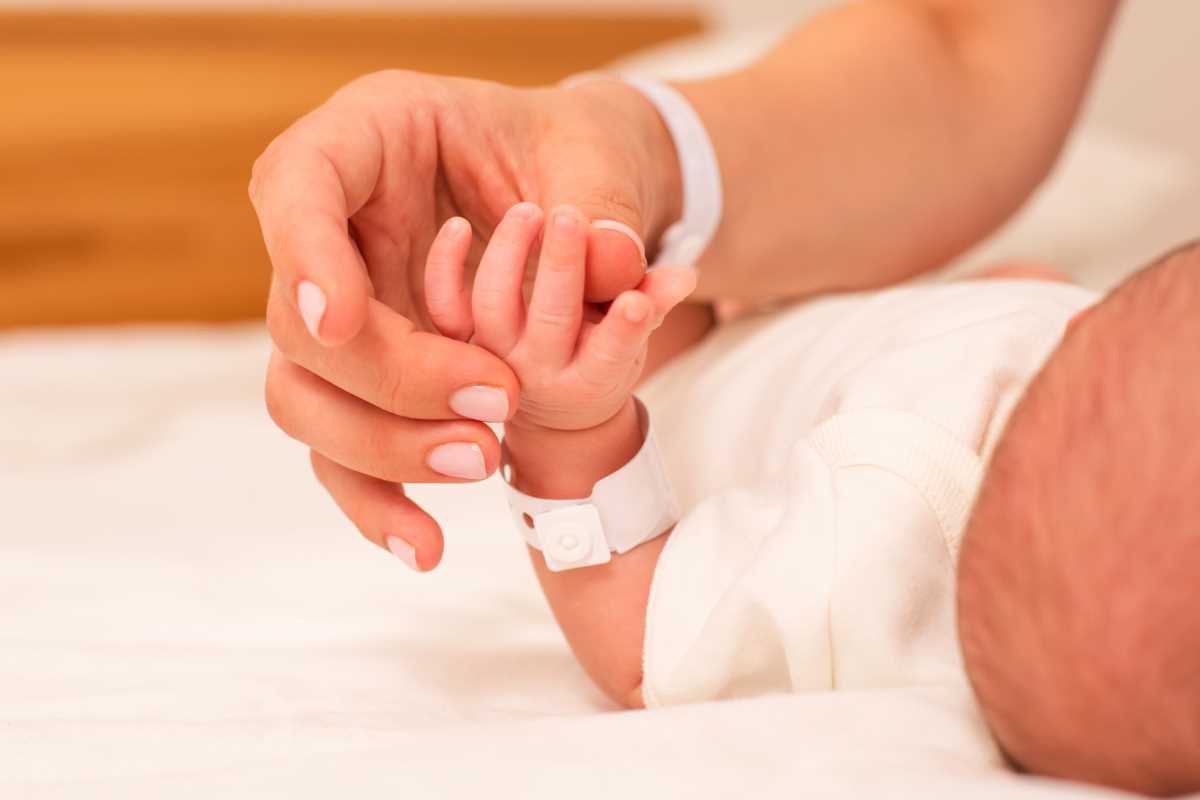
Bonding and Emotional Development
Breastfeeding is not just about nourishment; it also plays a crucial role in establishing a strong emotional bond between the mother and baby. The skin-to-skin contact, eye contact, and physical closeness experienced during breastfeeding promote feelings of security, comfort, and love. This intimate connection nurtures the baby's emotional development, fosters a sense of trust, and contributes to overall psychological well-being. Fact: Breastfeeding releases oxytocin, also known as the "love hormone," which promotes maternal-infant bonding.
Healthy Weight Management
Breastfeeding is associated with healthy weight management in both newborns and mothers. Breastfed babies are less likely to become overweight or obese later in life, thanks to the regulation of appetite hormones and the development of healthy eating habits early on. For mothers, breastfeeding helps burn extra calories, aiding in postpartum weight loss and reducing the risk of obesity-related health issues. Fact: Breastfeeding has been linked to a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes in mothers.
Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
The long-term benefits of breastfeeding extend beyond infancy, as it is associated with a reduced risk of chronic diseases later in life for both the baby and the mother. Breastfed babies are less likely to develop conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers due to the protective factors present in breast milk. For mothers, breastfeeding has been shown to lower the risk of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and osteoporosis. Fact: Breastfeeding is also linked to a lower incidence of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
In conclusion, the impact of breastfeeding on newborn development is truly remarkable, offering a host of benefits that promote optimal growth, health, and well-being. From providing essential nutrients and boosting immunity to fostering emotional bonding and reducing the risk of chronic diseases, breastfeeding plays a vital role in laying the foundation for a healthy start in life. It is a natural and invaluable gift that nourishes both the body and soul, creating a strong and lasting connection between mother and baby.
Featured image via oksix/Adobe Stock
 (Image via
(Image via